Free Inspection Checklist for Better Ladder Safety
Ladder safety should be a top priority for facilities and construction businesses of any size and level. Slips, trips and falls are still one of the leading causes of workplace fatalities, comprising approximately 25% of all worker deaths and 8% of non-fatal injuries annually, with many stemming from ladder falls. It's imperative for individuals to utilise the appropriate ladder type for each task and to employ it safely.
Choosing the Correct Ladder
Firstly, above all else, check whether using a ladder is absolutely necessary for completing the task. HSE recommends that if your task requires staying up a leaning ladder or stepladder for more than 30 minutes at a time, it is recommended you use alternative equipment. Carry out an assessment of the risk and only use a ladder when it has shown that using equipment that offers a higher level of fall protection is not justified.
Next, you need to choose the right tool for the job. There are 4 types of ladders that are most commonly used in the workplace. These are:
- Leaning Ladders – Leaning ladders are designed to lean against a stable surface for support rather than freestanding.
- Telescopic Ladders – Extendable ladders that can retract back to a small size. Similar to the handle of a luggage bag. These are a variation of leaning ladders, but they don’t work in the same way and some may be more prone to flexing and breakage.
- Stepladders – A self-supporting freestanding ladder with two sets of hinged legs connected by a hinged horizontal support bar, forming a triangular shape when opened. It typically has steps on one side and a flat platform on top. Great for tasks where no wall or structure is available for support.
- Combination and Multi-Purpose Ladders – Sometimes referred to as ‘A’ frame ladders, these types of ladders can be used in a variety of ways as step ladders, a variation of stepladders or leaning ladders.
Each performs a different function and should be used only in the intended situations for which it was built.
Ladder Safety Equipment Safety Checklist
Now that you have decided on the right ladder for the task at hand. You will want to run through the safety checklist below to ensure the ladder is still fit for purpose and you’re using it in the correct manner. We have also converted this into a FREE poster below for you to remind yourself of the necessary pre-use checks when needed!
Before using any ladder, you should have access to user instructions from the manufacturer in case you need them to refer back to. Before using the ladder conduct some checks to spot any visible defects to make sure it is safe.
Pre-Use Checklist
The person using the ladder should carry out a pre-use check at the beginning of the day and after something has changed. An example of this is when a ladder has been dropped or moved from a dirty area to a clean area.
This check needs to include:
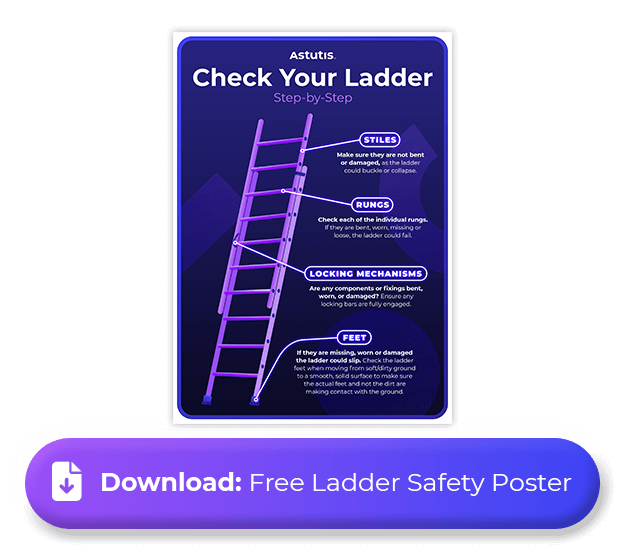
- Stiles: The rails running up both sides of the steps. Make sure they are not bent or damaged, as the ladder could buckle or collapse.
- Feet: The bottom of the ladder that typically has rubber covers. If they are missing, worn or damaged the ladder could slip. Check the ladder feet when moving from soft/dirty ground to a smooth, solid surface to make sure the actual feet and not the dirt are making contact with the ground.
- Rungs: Check each of the individual rungs/steps. If they are bent, worn, missing or loose, the ladder could fail.
- Locking Mechanisms: Any mechanism that looks the ladder in place. Are any components or fixings bent, worn, or damaged? Ensure any locking bars are fully engaged.
- Stepladder Platform (If Applicable): The platform on top of a stepladder. Check for any splits or buckles – anything that could cause it to become unstable or collapse.
- Steps or Treads on Stepladders (If Applicable): If they are contaminated, you could slip, and if the fixings are loose, they could collapse.
Ladder Use Checklist
In addition to checking the ladder, ensure you have considered the following when setting up the ladder:
- Stability: Make sure it placed on a stable/level surface - avoid uneven ground or slippery surfaces.
- Weight Capacity: Make sure the ladder is supported by your weight and any equipment or materials you will be carrying up it.
- Height: Is the ladder tall enough for the task at hand? Using a ladder that is too short increases the risk of falling.
- Clearance: Are there any overhead obstructions, such as power lines or tree branches, that could interfere with your movement?
- Weather Conditions: Is it windy or raining?
- Footwear: Wear appropriate shoes to prevent slipping, etc.
- Buddy System: Do you need an additional person to spot the ladder and ensure it stays stable?
All these are additional measures that will help to ensure your safety even further.
Where Can You Learn More About Ladder Safety?
Ladder safety is very important to several different industries to mitigate and prevent falls from heights. The IOSH Managing Safely is considered the perfect starting point to learn about different hazards that can cause slips, trips and falls. In addition to this, learners will have access to a library of other topics related to health and safety.
Upon completion of the course, learners will know how to:
- Identify how the law can have an impact on safety and health in the workplace.
- Identify workplace hazards and risks, their impact and how to manage them.
- Identify how to evaluate and respond to an incident.
- List the benefits and characteristics of an effective health and safety management system.
- Describe the principles that underpin good safety and health performance.
Both employers and employees can reap a number of benefits from the IOSH Managing Safely, such as ensuring compliance with legislation, avoiding fines and lost productivity, and, of course, protecting themselves and their co-workers from harm.

Real Life Stories